Purpose
- Deliver low to moderate levels of oxygen to relieve hypoxia.
Assessment/Preparation
- Assess respiratory status (i.e., breath sounds, respiratory rate and depth, presence of sputum, arterial blood gases if available).
- Assess past medical history, noting chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD). For clients with COPD, hypoxemia is often the stimulus to breathe because they chronically have high blood levels of carbon dioxide. If additional oxygen is needed, a low-flow system is essential to maintain slight hypoxemia so breathing is stimulated.
- Assess for clinical signs and symptoms of hypoxia: anxiety, decreased level of consciousness, inability to concentrate, fatigue, dizziness, cardiac dysrhythmias, pallor or cyanosis, dyspnea.
Equipment
- Approproate oxygen delivery system:
- Simple oxygen mask (O2 concentrations: 40%-60%)
- Venturi mask - delivers O2 concentrations accurate within 1% (24%-50%). Frequently used with clients with COPD.
- Partial rebreather mask - low flow system (O2 concentrations: 50%-70%). Reservoir bag allows client to rebreathe a portion of exhaled air. (Bag must not totally deflate during inspiration, or O2 flow rate should be increased.)
- Nonrebreather mask - delivers the highest O2 concentrations possible without mechanical ventialation (80%-90%). One-way valve prevents room air or exhaled air from being inspired.
- Oxygen source
- Flowmeter
- "No smoking" sign
- Humidifier and distilled water (for high-flow O2 therapy)
Procedure
-
Review chart for physician's order for oxygen to ensure that it includes method of delivery, flow rate, titration orders; identify client.
Rationale: Prevents potential errors.
-
Wash your hands.
Rationale: Handwashing reduces transmission of microorganisms.
-
Identify client and proceed with 5 rights of medication administration. Explain procedure to client. Explain that oxygen will ease dyspnea or discomfort, and inform client concerning safety precautions associated with oxygen use.
Rationale: Oxygen is a drug and administering using the 5 rights avoids potential errors. Teaching helps ensure compliance with therapy.
-
Assist client to semi- or high Fowler's position, if tolerated.
Rationale: These positions facilitate optimal lung expansion.
-
Insert flowmeter into wall outlet. Attach oxygen tubing to nozzle on flowmeter (Fig. 1). If using a high O2 flow, attach humidifier. Attach oxygen tubing to humidifier.
Rationale: Oxygen in high concentrations can be drying to the mucosa.
-
Turn on the oxygen at the prescribed rate (Fig. 2). For a mask with a reservoir, be sure to allow oxygen to fill bag (Fig. 3).
Rationale: Oxygen must be administered as prescribed.
- Place mask on face, applying from the nose and over the chin (Fig. 4).
- Adjust the metal rim over the nose and contour the mask to the face.
-
Adjust the metal rim over the nose and contour the mask to the face (Fig. 5).
Rationale: Client is more likely to comply with therapy if equipment fits comfortably.
-
Assess for proper functioning of equipment and observe client's initial response to therapy.
Rationale: Assessment of vital signs, oxygen saturation, color, breathing pattern, and orientation helps the nurse evaluate effectiveness of therapy and detect clinical evidence of hypoxia.
-
Monitor continuous therapy by assessing for pressure areas on the skin and nares every 2 hours and rechecking flow rate every 4 to 8 hours.
Rationale: Permit early detection of skin breakdown or inadequate flow rate.
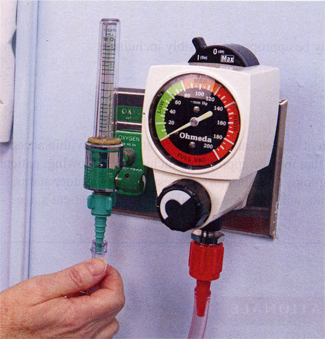
Fig. 1: Conect face mask to oxygen source.

Fig. 2: Adjust flow rate.

Fig. 3: Allow oxygen to fill the bag.

Fig. 4: Oxygen mask applied over nose and mouth.
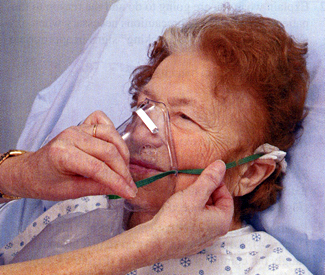
Fig. 5: Adjust elastic strap.
| Sample Documentation | |||
| 12/19/10 | 0400 | Client reports shortness of breath. Skin pale. Respirations 30 breaths per minutes and labored. Lungs sounds decreased throughout. Oxygen saturation via pulse oximeter 88%. Oxygen via nonrebreather face mask applied at 12 L/min as ordered. After O2 applied, respirations even and unlabored. Skin is pink. Respiration rate is 18 breaths per min. Lungs remain with decreased breath sounds throughout. Oxygen saturation increased to 98%. Danielle Williams, RN | |
Lifespan Considerations
Infant and Child- Isolettes (incubators) and tents may be used for administering oxygen and humidity to infants and newborns. It is difficult to maintain high concentrations of oxygen in an isolette or tent, but it is nonintrusive and nonirritating.
- Plan nursing care so tent or isolette is entered as little as possible to prevent oxygen levels from dropping.
- Children frightened by the oxygen tent may feel more secure with their favorite toy or blanket.
Home Care Modifications
- In-home oxygen supply is delivered by cylinders, liquid oxygen, or oxygen concentrators. Portable oxygen systems are available to increase independence and social activities.
- Equipment vendor and home care nurse should instruct client on how to use home oxygen equipment and how often the equipment must be filled.
- Instruct the client and family about the importance of not smoking in the area of oxygen use.
-
The client should be informed about using an oxygen vendor whose services include:
- Trained personnel to instruct the client in use and maintenance of the equipment
- 24-hour emergency service
- Monthly follow-up visits for equipment maintenance and client instruction
- Vendor insurance billing
- Needing oxygen at home can be stressful for the client. Clients should be encouraged to share their fears and concerns. A local support group of clients using home oxygen may help them to discuss their feelings.
- For insurance to cover home oxygen, clients must have oxygen saturation below 88% to 90% on room air.