Purpose
- Measure peak expiratory flow rate (PEFR), which is the point of highest flow during maximal exhalation.
- Better control asthma by quickly detecting subtle changes in airway diameter so preventive interventions can be instituted.
- Provide objective data to assess respiratory function.
Assessment
- Identify clients who would benefit from or have been prescribed peak flow monitoring (e.g., clients with asthma).
- Assess client's baseline oxygenation status including vital signs, skin and nailbed color, breath sounds, shortness of breath, alterations in breathing pattern, cognitive changes.
- Note any subjective verbalizations regarding respiratory status (e.g., tightness in the chest, more difficult to breathe).
- Note new or recent exposure to factors that could alter airway diameter (e.g., smoke, chemicals, animal dander, pollens, and molds).
- Note any use of medications that could alter airway diameter (e.g., sympathomimetics, anticholinergics, corticosteroids).
Equipment
- Peak flowmeter
- Charts to calculate green, yellow, and red zones based on personal best data
Procedure
-
Verify the physician order and identify the client.
Rationale: Prevents potential errors.
-
Explain the purpose of peak flow monitoring to the client and family (Fig. 1).
Rationale: Understanding the procedure increases compliance and decreases anxiety. Measurements taken before using bronchodilators will provide more accurate data regarding baseline airway diameter.
-
Place indicator at the base of the numbered scale. Have client stand up.
Rationale: Having indicator in the correct position will ensure accurate measurement of peak expiratory flow. Standing position allows full expansion of lungs.
-
Tell the client to take a deep breath. Place the meter in his or her mouth. The client should close the lips around the mouthpiece (Fig. 2). Remind the client not to put the tongue in the hole.
Rationale: Close fit around the mouthpiece and unobstructed mouthpiece are necessary for proper measurement of exhaled air.
-
Tell the client to exhale as fast and as hard as he or she can, keeping a tight fit around the mouthpiece (Fig. 3).
Rationale: Motivation and proper technique will obtain highest peak flow.
-
Repeat steps 2 through 4 twice more, and record the highest peak flow obtained in the three attempts (Fig. 4).
Rationale: Peak flow varies from one attempt to another. The highest number represents the client's best effort.
-
To determine "personal best" when beginning peak flow monitoring, obtain peak flow measurements in the morning and again in the evening over a 2-week period of good asthma control (feel good without any asthma symptoms). The client should take measurements before using bronchodilators.
Rationale: "Personal best" represents the client's best effort during a period of good control. This will provide a baseline from which to predict green, yellow, and red zones.
-
Healthcare provider will calculate zones based on percentage of personal best (green 80%-100%; yellow 50%-80%; red below 50%) and give instructions for what to do when in each zone.
Rationale: Zones determine how well asthma is controlled and provide guidelines for client to adjust treatment or contact healthcare provider.
-
Encourage client to comply with twice-a-day (morning and evening) peak flow monitoring before bronchodilator therapy and follow healthcare provider's instructions for peak flows in each zone. Follow steps 2 through 5.
Rationale: Consistent use of peak flow monitoring allows the client to detect subtle changes in airway diameter and institute appropriate therapy to avoid acute asthma exacerbations.
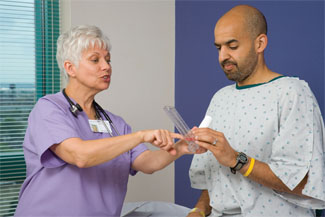
Fig. 1: Explain purpose of peak flow monitoring.
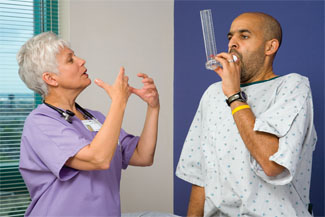
Fig. 2: Verbally encourage client to take a deep breath and place
meter in mouth.
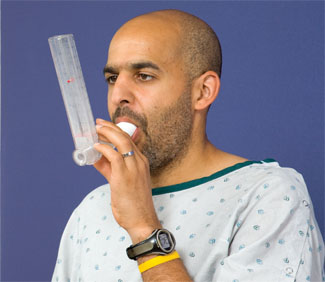
Fig. 3: Have client exhale as fast and hard as he or she can.

Fig. 4: Record highest peak flow obtained in three attempts.
| Sample Documentation | |||
| 12/12/10 | 0900 |
P: Health management of newly diagnosed asthma, hospitalized 2 weeks ago. I: RT instructed use of peak flow meter and obtained baseline values, calculating green, yellow, and red zones. E: Client and wife could verbalize what to do when peak flows fell into each zone. Nursing will follow-up at next appointment. S. Roberts, RN |
|
Lifespan Considerations
Child and Adolescent- Peak flow monitoring is appropriate for children who are able to follow directions and use effective technique. Baseline values need to be recalculated every 6 months during growth spurts. Children may need reminders from family members and help keeping a daily log. Adolescents need to assume more responsibility and control over their asthma management.
Home Care Modifications
- Most peak flow monitoring is done in the home setting. Initial teaching is usually done in the clinic or physician's office. Follow-up is important. Home care nurses use peak